4. Approximate and subdivide polygon chains¶
This example shows how to approximate (Douglas-Peucker algorithm) and subdivide (B-Splines) polygonal chains.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.measure import approximate_polygon, subdivide_polygon
4.1. Create the test object¶
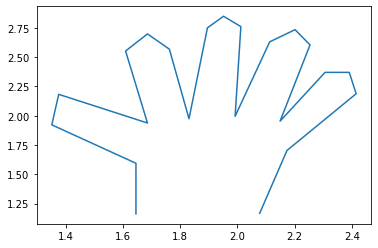
hand = np.array([[1.64516129, 1.16145833],
[1.64516129, 1.59375],
[1.35080645, 1.921875],
[1.375, 2.18229167],
[1.68548387, 1.9375],
[1.60887097, 2.55208333],
[1.68548387, 2.69791667],
[1.76209677, 2.56770833],
[1.83064516, 1.97395833],
[1.89516129, 2.75],
[1.9516129, 2.84895833],
[2.01209677, 2.76041667],
[1.99193548, 1.99479167],
[2.11290323, 2.63020833],
[2.2016129, 2.734375],
[2.25403226, 2.60416667],
[2.14919355, 1.953125],
[2.30645161, 2.36979167],
[2.39112903, 2.36979167],
[2.41532258, 2.1875],
[2.1733871, 1.703125],
[2.07782258, 1.16666667]])
plt.plot(hand[:, 0], hand[:, 1])
plt.show()
4.2. Subdivide polygon using 2nd degree B-Splines¶
new_hand = hand.copy()
for _ in range(5):
new_hand = subdivide_polygon(new_hand, degree=2, preserve_ends=True)
4.3. Approximate subdivided polygon with Douglas-Peucker algorithm¶
appr_hand = approximate_polygon(new_hand, tolerance=0.02)
4.4. Show¶
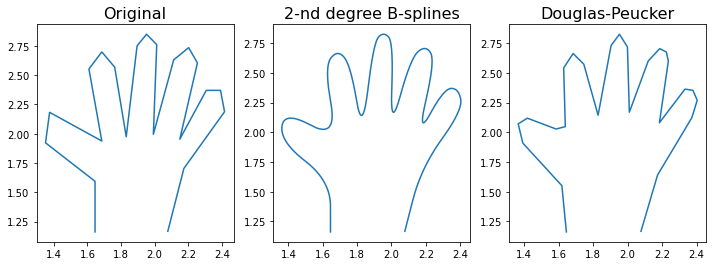
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(ncols=3, figsize=(12, 4))
ax1.plot(hand[:, 0], hand[:, 1])
ax1.set_title("Original",fontsize=16)
ax2.plot(new_hand[:, 0], new_hand[:, 1])
ax2.set_title("2-nd degree B-splines",fontsize=16)
ax3.plot(appr_hand[:, 0], appr_hand[:, 1])
ax3.set_title("Douglas-Peucker",fontsize=16)
plt.show()
plt.plot(hand[:, 0], hand[:, 1])
plt.plot(new_hand[:, 0], new_hand[:, 1])
plt.plot(appr_hand[:, 0], appr_hand[:, 1])
plt.show()